At the moment, not all browsers understand the current JavaScript version but all ES5, which means that developers can not write or write completely in ES6 or higher. Since you would have to optimize each browser by work around or on just the existing features in ES6 or higher.
As a developer you do not want to be behind but ahead. This means staying up-to-date and trying out the latest technology, the latest development, the latest platform or even the newest framework. There is the compiler TypeScript from Microsoft and so we can code with the most recent version of JavaScript.
ECMA International
Why use TypeScript?
Not only can we code in the latest version, we can also use types as the name implies. That is, we can define data types such as string, number, or even boolean. So we get errors like wrong data handed over not in runtime, but already in our development environment and can fix them in time.
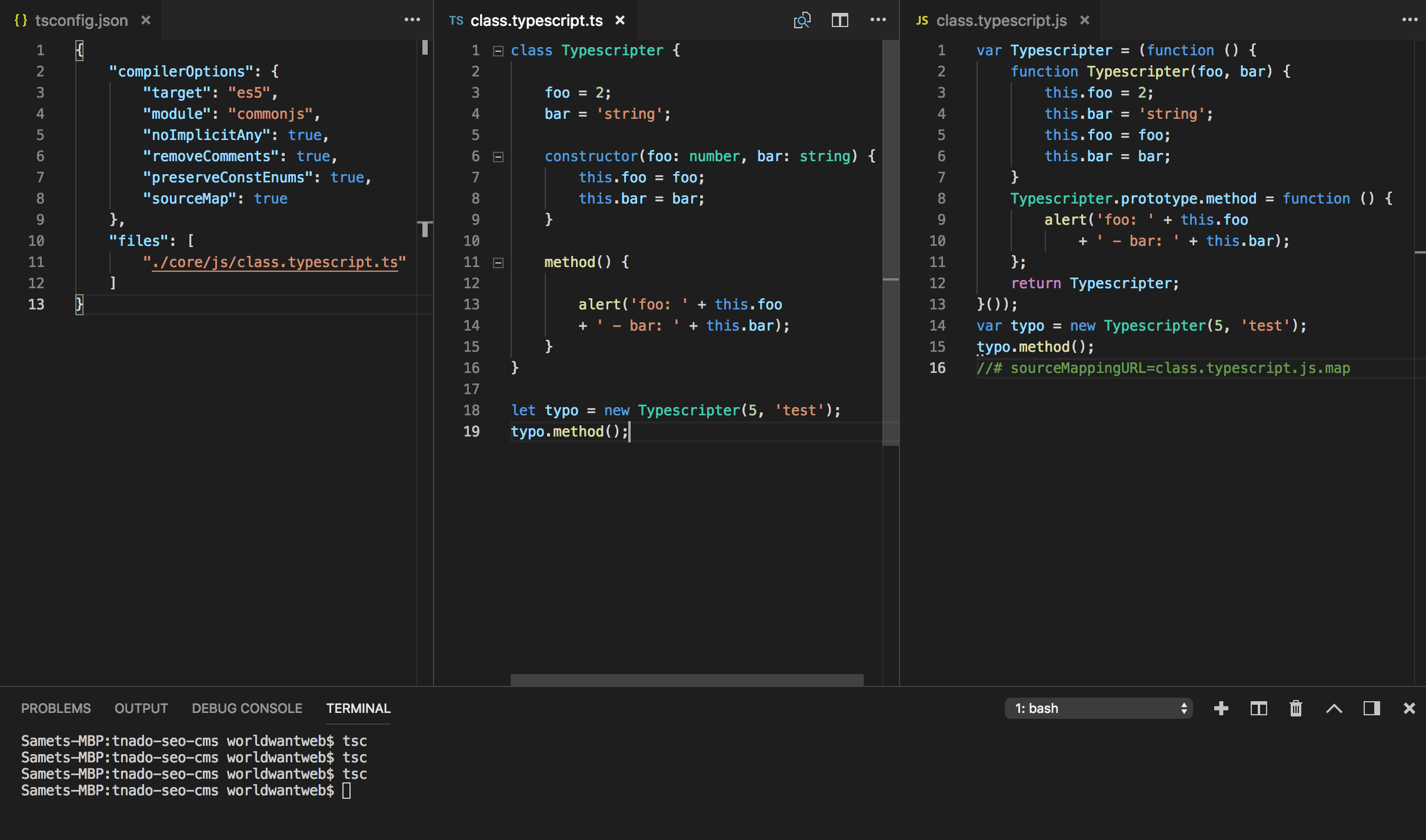
0 constructor(foo: number, bar: string) { Install TypeScript with this tutorial
To install TypeScript you need first Node.js Download it and install it on your operating system. Then just do it USERNAME$ npm install -g typescript So you have already done the installation if your editor Visual Studio Code means, if not then you probably need a few more steps or you decide for VSC. In this case, we have the VSC Editor from Microsoft and thus directly TypeScript on board.
Configuration of the tsconfig
For the configuration we need the tsconfig.json with which we communicate TypeScript options and more. And this could look like this where we have e.g. set to transpare to an older version of JS or even remove comments.
0 { 1 "compilerOptions": { 2 "target": "es5", 3 "module": "commonjs", 4 "noImplicitAny": true, 5 "removeComments": true, 6 "preserveConstEnums": true, 7 "sourceMap": true 8 }, 9 "files": [ 10 "./core/js/class.typescript.ts" 11 ] 12 } Thus, we would have completed our configuration and can get started.
Code and transpilate
Now we create a new TypeScript file and name it as well as our JavaScript file will be called with the extension ts, for example script.ts In the TypeScript file we can now code with the most recent JavaScript version :), here is a small example
0 class Typescripter { 1 2 foo = 2; 3 bar = 'string'; 4 5 constructor(foo: number, bar: string) { 6 this.foo = foo; 7 this.bar = bar; 8 } 9 10 method() { 11 12 alert('foo: ' + this.foo 13 + ' - bar: ' + this.bar); 14 } 15 } 16 17 let typo = new Typescripter(5, 'test'); 18 typo.method(); When we have written our code, we open our console and enter the following USERNAME$ tsc if in the tsconfig.json files was not specified there must be the path USERNAME$ tsc path/script.ts be specified. After transpiling, the created JavaScript version is located script.js in the same folder.
0 var Typescripter = (function () { 1 function Typescripter(foo, bar) { 2 this.foo = 2; 3 this.bar = 'string'; 4 this.foo = foo; 5 this.bar = bar; 6 } 7 Typescripter.prototype.method = function () { 8 alert('foo: ' + this.foo 9 + ' - bar: ' + this.bar); 10 }; 11 return Typescripter; 12 }()); 13 var typo = new Typescripter(5, 'test'); 14 typo.method(); 15 //# sourceMappingURL=class.typescript.js.map Try it right now to code with the latest and most recent JavaScript version.
Expand the possibilities
To go further, we could still benefit from other frameworks and get a lot more out of our environment. This means we expand our environment so that we work more browser specific. Some frameworks allow us to execute and compile them directly in the browser, but this also means more performance loss again. That's why we use everything here in our development environment and the example for it could look like this.
- Use the Typescript compiler to compile TypeScript into a current version of JavaScript without providing backward compatibility or browser polyfilling.
- Use the Babel compiler to convert a newer version of JavaScript that browsers can not directly execute into a version that browsers can run.
- Use the Webpack or FuseBox to sort and bundle your files, which you can organize at will for development a simpler package for everything. A smaller solution is Parcel.
So you see it is even more possible and we will also go into these things in the following TypeScript tutorials. So if you want to hear this, sign up for our newsletter or subscribe to one of our social networks.
Here is coming more for Webpack, TypeScript Tutorials and more, follow this page:
Webpack Project Examples
Generate Webpack with TypeScript, Preact, Redux-Zero and Babel
Advertising